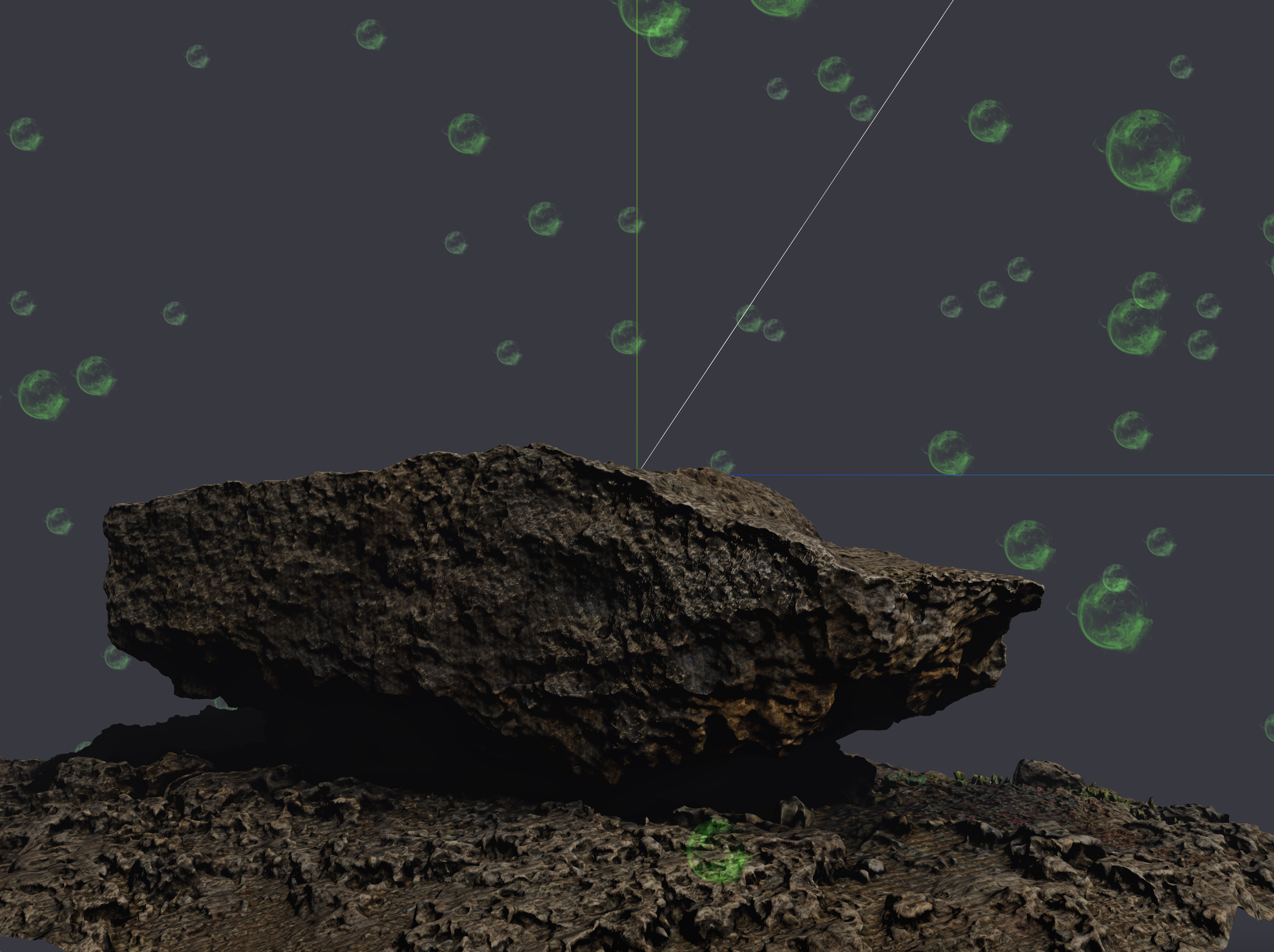
Particle 로 반딧불이 표현하기
반딧불이나 별은 매우 많은 입자들로 표현합니다.
이를 3D 그래픽스에서는 Particle 이라고 합니다.
각각의 입자를 개별 Mesh 로 구현한다면 화면이 버벅이거나 실행할 수 없는 경우까지 발생할 수 있습니다.
이번 포스팅에서는 컴퓨터 성능을 저해하지 않으면서 Particle 을 구현하는 방법에 대해 정리하고자 합니다.
예시 코드
이번 포스팅의 예시코드는 위 모델을 렌더링한 시점입니다.
// three.js
import {
WebGLRenderer,
ACESFilmicToneMapping,
Scene,
PerspectiveCamera,
AxesHelper,
Color,
DirectionalLight,
DirectionalLightHelper,
} from 'three';
// three.js - addons
import {
OrbitControls,
} from 'three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls';
import {
GLTFLoader,
} from 'three/examples/jsm/loaders/GLTFLoader';
// style
import './style.css';
//
// state
//
/** @type { WebGLRenderer } */
let renderer;
/** @type { Scene } */
let scene;
/** @type { PerspectiveCamera } */
let camera;
/** @type { OrbitControls } */
let controls;
//
// core
//
function initCanvas() {
const $canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
const $app = document.querySelector('#app');
$app?.appendChild($canvas);
return $canvas;
}
function initRenderer($canvas) {
renderer = new WebGLRenderer({
canvas: $canvas,
antialias: true,
});
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
renderer.toneMapping = ACESFilmicToneMapping;
renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true;
}
function initScene() {
scene = new Scene();
}
function initCamera() {
camera = new PerspectiveCamera();
camera.fov = 30;
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
camera.near = 0.5;
camera.far = 2_000;
camera.position.set(0, 0, 5);
camera.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
}
function initAxesHelper() {
const helper = new AxesHelper(1);
scene.add(helper);
}
function initControls($target) {
controls = new OrbitControls(camera, $target);
controls.enableDamping = true;
}
//
// light
//
function initDirectionalLight() {
const color = new Color('#fff');
const light = new DirectionalLight(
color,
Math.PI * 1
);
light.position.set(-2, 2, 1);
light.lookAt(0, 0, 0);
light.castShadow = true;
const helper = new DirectionalLightHelper(light);
scene.add(light);
scene.add(helper);
}
//
// model
//
function initModel() {
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.load('/gltf/coast-rocks-05/coast_rocks_05_4k.gltf', gltf => {
const model = gltf.scene;
model.position.set(0, -0.5, 0);
model.traverse(child => {
if (!child.isMesh) {
return;
}
child.castShadow = true;
child.receiveShadow = true;
});
scene.add(model);
});
}
//
// executor
//
function render() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(render);
renderer.render(scene, camera);
controls?.update();
}
(function init() {
const $canvas = initCanvas();
initRenderer($canvas);
initScene();
initCamera();
initAxesHelper();
initControls($canvas);
initDirectionalLight();
initModel();
render();
}());
Particle 구현 흐름
3D 환경에서 물체를 렌더링하기 위해, Geometry 와 Material 을 조합한 Mesh 를 사용합니다.
Particle 은 Mesh 가 아닌 Points 객체로 만들 수 있습니다.
Points 를 생성할 때도 Mesh 처럼 Geometry 와 Material 이 필요합니다.
Particle 을 만드는 과정을 간략하게 표현하면 다음과 같습니다.
- BufferGeometry 객체 생성하기
- PointsMaterial 객체 생성하기
- BufferGeometry 와 PointsMaterial 을 인자로 사용하여 Points 객체 생성하기
scene.add()로 등록하기
1. BufferGeometry 만들기
Particle 의 Geometry 는 BufferGeometry 로 만들 수 있습니다.
BufferGeometry 는 buffer 라는 개념을 사용한 Geometry 이며, 다음과 같은 과정으로 생성합니다.
- Float32Array 객체 생성
- Float32Array 를 사용하여 BufferAttribute 객체 생성
- BufferGeometry 객체 생성
- BufferGeometry 의 position 속성에 BufferGeometry 적용
1. Float32Array 객체 생성
Float32Array 는 형식화 배열 입니다.
자바스크립트의 Array 는 배열 길이를 동적으로 사용할 수 있고, Tuple 로도 활용할 수 있습니다.
형식화 배열은 Java 와 같은 정적 언어의 배열처럼 고정된 길이의 Array 입니다.
참고로 형식화 배열은 자바스크립트에서 Array 와 구분하고 있으며, 형식화_배열.__proto__.isArray() 는 false 를 반환합니다.
Float32Array 는 부동소수로 구성된 형식화 배열 입니다.
비디오나 오디오와 같은 리소스를 빠르게 제어하기 위해 사용되는 빌트인 객체 입니다.
우리가 생성할 buffer 는 각 Particle 입자들의 x, y, z 좌표값으로 생성할 예정입니다.
아래는 buffer 의 예시이며, 1차원 배열에 x, y, z 좌표값이 순서대로 나열된 형태 입니다.
[
x1, y1, z1,
x2, y2, z2,
x3, y3, z3,
]500개의 Particle 을 표현하기 위한 Float32Array 를 생성하면 다음과 같습니다.
//
// particle
//
const PARTICLE_AXIS = {
X: 0,
Y: 1,
Z: 2,
};
function initParticle() {
const buffer = new Float32Array(Array.from(
// 3개의 요소가 Particle 1개의 x, y, z 좌표값이 되며, 500 개를 생성합니다.
{ length: 3 * 500 },
(_, i) => {
const randomValue = Math.random();
const axis = i % 3;
switch (axis) {
case PARTICLE_AXIS.X:
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Z:
return (randomValue * 2 - 1) * 2;
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Y:
default:
return randomValue * 2;
}
}
));
}2. Float32Array 를 사용하여 BufferAttribute 객체 생성
BufferGeometry 는 Particle 의 Geometry 로 활용됩니다.
BufferGeometry 에 buffer 를 직접 적용할 수는 없고, BufferAttribute 객체를 통해서만 적용할 수 있습니다.
// three.js
import {
WebGLRenderer,
ACESFilmicToneMapping,
Scene,
PerspectiveCamera,
AxesHelper,
Color,
DirectionalLight,
DirectionalLightHelper,
BufferAttribute,
} from 'three';//
// particle
//
const PARTICLE_AXIS = {
X: 0,
Y: 1,
Z: 2,
};
function initParticle() {
const buffer = new Float32Array(Array.from(
{ length: 3 * 500 },
(_, i) => {
const randomValue = Math.random();
const axis = i % 3;
switch (axis) {
case PARTICLE_AXIS.X:
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Z:
return (randomValue * 2 - 1) * 2;
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Y:
default:
return randomValue * 2;
}
}
));
const positionAttribute = new BufferAttribute(buffer, 3);
}BufferAttribute 생성자는 다음과 같은 interface 를 가집니다.
class BufferAttribute {
constructor(
// 형식화 배열
array: TypedArray,
// 입자 하나를 이루는 요소(좌표값) 개수
itemSize: number
);
}우리가 생성한 buffer 는 x, y, z 3개의 좌표가 1개의 입자를 표현하므로, 아래와 같이 BufferAttribute 를 생성하였습니다.
const positionAttribute = new BufferAttribute(buffer, 3);3. BufferGeometry 객체 생성
BufferGeometry 객체를 생성해 보겠습니다.
// three.js
import {
WebGLRenderer,
ACESFilmicToneMapping,
Scene,
PerspectiveCamera,
AxesHelper,
Color,
DirectionalLight,
DirectionalLightHelper,
BufferAttribute,
BufferGeometry,
} from 'three';//
// particle
//
const PARTICLE_AXIS = {
X: 0,
Y: 1,
Z: 2,
};
function initParticle() {
const buffer = new Float32Array(Array.from(
{ length: 3 * 500 },
(_, i) => {
const randomValue = Math.random();
const axis = i % 3;
switch (axis) {
case PARTICLE_AXIS.X:
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Z:
return (randomValue * 2 - 1) * 2;
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Y:
default:
return randomValue * 2;
}
}
));
const positionAttribute = new BufferAttribute(buffer, 3);
const geometry = new BufferGeometry();
}4. BufferGeometry 의 position 속성에 BufferGeometry 적용
BufferGeometry 객체는 setAttribute('속성명', BufferAttribute_객체) 메소드를 사용하여 프로퍼티를 변경할 수 있습니다.
BufferGeometry 의 attribute 중, 좌표값은 'position' 으로 사용합니다.
//
// particle
//
const PARTICLE_AXIS = {
X: 0,
Y: 1,
Z: 2,
};
function initParticle() {
const buffer = new Float32Array(Array.from(
{ length: 3 * 500 },
(_, i) => {
const randomValue = Math.random();
const axis = i % 3;
switch (axis) {
case PARTICLE_AXIS.X:
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Z:
return (randomValue * 2 - 1) * 2;
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Y:
default:
return randomValue * 2;
}
}
));
const positionAttribute = new BufferAttribute(buffer, 3);
const geometry = new BufferGeometry();
geometry.setAttribute('position', positionAttribute);
}2. PointsMaterial 객체 생성 및 Particle 렌더링하기
Particle 의 Material 은 PointsMaterial 을 사용합니다.
각 Particle 의 재질에 이미지 파일 을 패턴으로 사용하도록 만들고자 합니다.
PointsMaterial 과 BufferGeometry 를 생성하였으므로, Points 객체를 생성하여 Particle 을 렌더링할 수 있습니다.
// three.js
import {
WebGLRenderer,
ACESFilmicToneMapping,
Scene,
PerspectiveCamera,
AxesHelper,
Color,
DirectionalLight,
DirectionalLightHelper,
BufferAttribute,
BufferGeometry,
PointsMaterial,
TextureLoader,
Points,
} from 'three';//
// particle
//
const PARTICLE_AXIS = {
X: 0,
Y: 1,
Z: 2,
};
function initParticle() {
const buffer = new Float32Array(Array.from(
{ length: 3 * 500 },
(_, i) => {
const randomValue = Math.random();
const axis = i % 3;
switch (axis) {
case PARTICLE_AXIS.X:
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Z:
return (randomValue * 2 - 1) * 2;
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Y:
default:
return randomValue * 2;
}
}
));
const positionAttribute = new BufferAttribute(buffer, 3);
const geometry = new BufferGeometry();
geometry.setAttribute('position', positionAttribute);
const material = new PointsMaterial({
map: new TextureLoader().load('/particle/circle.png'),
size: 1,
});
const particle = new Points(geometry, material);
scene.add(particle);
}
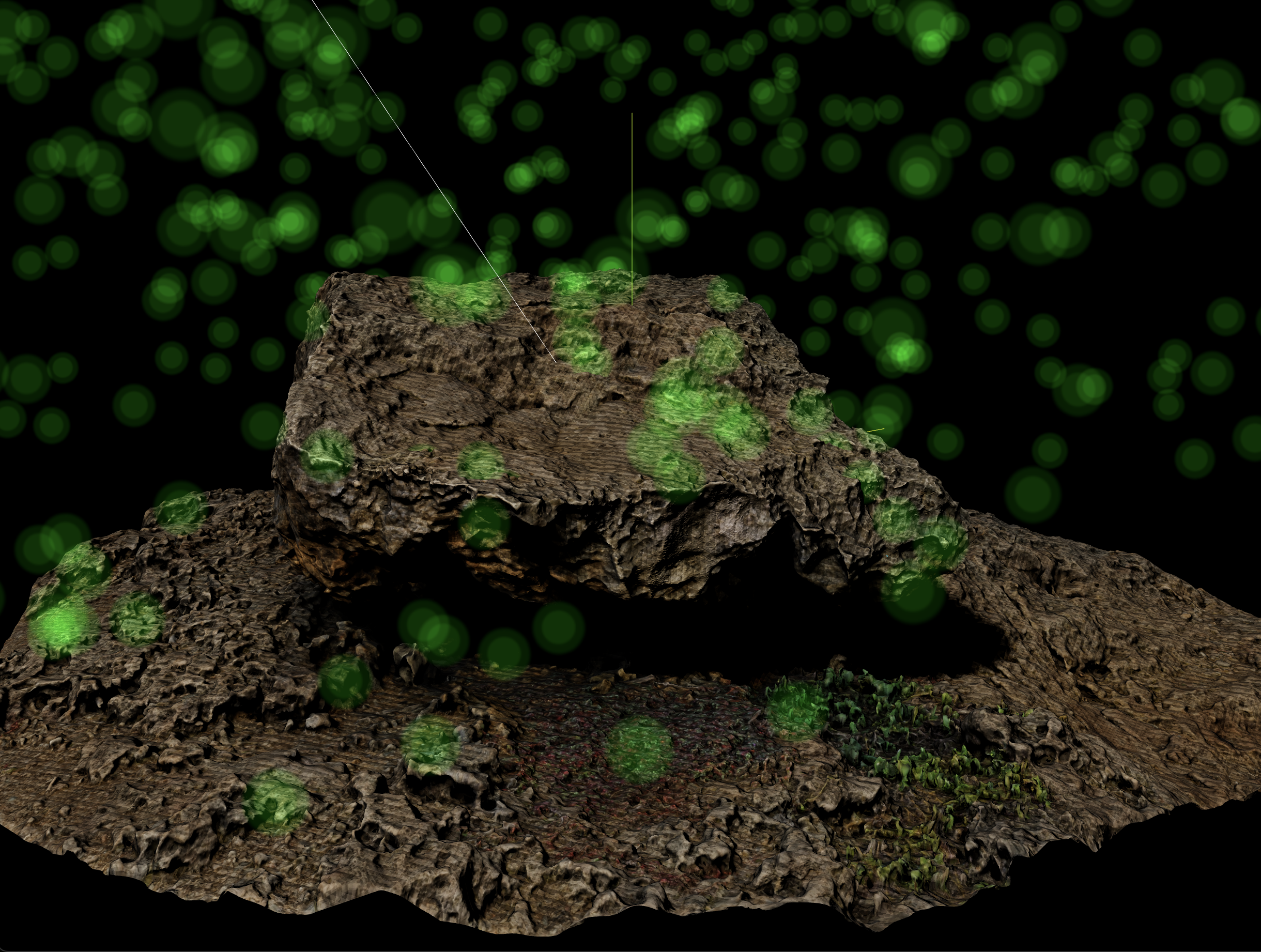
위 코드에서 PointsMaterial 을 생성하는 부분을 살펴보겠습니다.
PointsMaterial 생성자에 넘겨준 params 에 map 속성이 있습니다.
map 속성을 사용하여 Particle 하나에 적용시킬 이미지를 Texture 로 넘겨줄 수 있습니다.
const loader = new TextureLoader();
const texture = loader.load('이미지_경로');우리가 넘겨준 이미지는 배경을 투명하게 처리한 png 임에도 불구하고, 렌더링 결과에는 이미지의 투명도가 적용되지 않은 상태 입니다.
이를 해결하기 위해, PointsMaterial 생성자 params 에 추가 설정이 필요합니다.
아래와 같이 추가해 보겠습니다.
// three.js
import {
WebGLRenderer,
ACESFilmicToneMapping,
Scene,
PerspectiveCamera,
AxesHelper,
Color,
DirectionalLight,
DirectionalLightHelper,
BufferAttribute,
BufferGeometry,
PointsMaterial,
TextureLoader,
Points,
AdditiveBlending,
} from 'three';//
// particle
//
const PARTICLE_AXIS = {
X: 0,
Y: 1,
Z: 2,
};
function initParticle() {
const buffer = new Float32Array(Array.from(
{ length: 3 * 500 },
(_, i) => {
const randomValue = Math.random();
const axis = i % 3;
switch (axis) {
case PARTICLE_AXIS.X:
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Z:
return (randomValue * 2 - 1) * 2;
case PARTICLE_AXIS.Y:
default:
return randomValue * 2;
}
}
));
const positionAttribute = new BufferAttribute(buffer, 3);
const geometry = new BufferGeometry();
geometry.setAttribute('position', positionAttribute);
const material = new PointsMaterial({
map: new TextureLoader().load('/particle/circle.png'),
// Particle 1개의 크기
size: 0.5,
// Particle 색상
color: new Color('#006400'),
// Particle 투명도
opacity: 0.5,
// 투명도 사용여부
transparent: true,
// Particle 과 겹치는 부분의 색상을 처리(섞는) 방식 설정
blending: AdditiveBlending,
// Particle 의 깊이 표현 여부
depthWrite: false,
});
const particle = new Points(geometry, material);
scene.add(particle);
}
PointsMaterial 에 투명도를 설정할 때는 아래의 설정이 함께 필요합니다.
transparent: trueblending: AdditiveBlendingdepthWrite: true
마치며
Three.js 의 Particle 생성 방법을 스터디하기 전까지는 개별 Particle 요소를 하나하나 만들어야 하는 것 같았습니다.
이번 포스팅을 통해 Particle 을 효과적으로 활용할 수 있을 것 같습니다.
다만 위 예제처럼 scene.background 와 scene.fog 를 어두운 색(#383841) 일 경우에 한하여 의도한 결과가 렌더링되었습니다.
scene.background 와 scene.fog 를 밝은 색상으로 설정하면, 여전히 Particle 의 외곽선이 보이는 현상이 있습니다.
차후 관련하여 좀 더 찾아본 후, 해결방법을 정리하겠습니다.
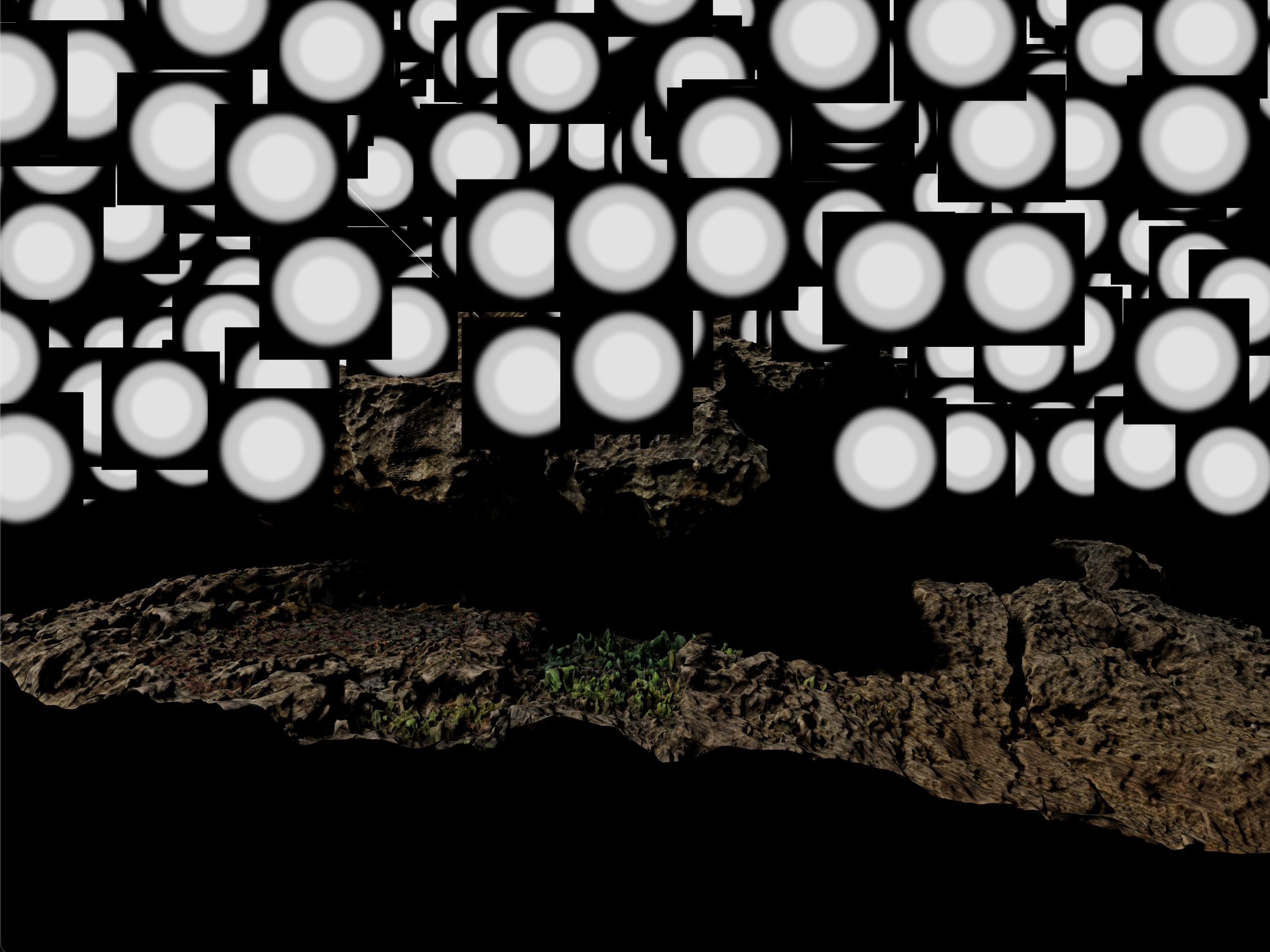
(Issue 해결) Particle 의 배경이 보이는 현상
위 예시에서 사용한 png 파일을 확인한 결과, 배경이 투명이 아닌 검은색이었습니다.
배경이 투명하게 처리된 png 파일을 사용하면 정상적으로 렌더릴 되었습니다.